Difference between revisions of "Getting started in VBA"
From Ribbon Commander Documentation
(→Writing some code!) |
(→Referencing the library) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
# The library is now ready to use. In the immediate window enter | # The library is now ready to use. In the immediate window enter | ||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="vb">?rxCustomUI.defaultInstance.targetOfficeVersion</syntaxhighlight> | #: <syntaxhighlight lang="vb">?rxCustomUI.defaultInstance.targetOfficeVersion</syntaxhighlight> | ||
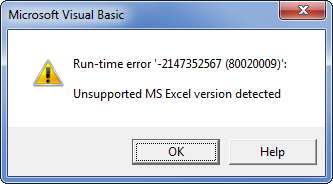
| − | #: This should print the major version of the office platform you are using. If you are running in an older version of office you will get a runtime error instead (the error message is for excel | + | #: This should print the major version of the office platform you are using. If you are running in an older version of office you will get a runtime error instead (the error message here is for excel) |
#: [[image:UnsupportedExcelVersion.png]] | #: [[image:UnsupportedExcelVersion.png]] | ||
Revision as of 03:22, 11 March 2013
Prerequisites
Before you get started install Dynamic RibbonX on your PC (see Installation)
Referencing the library
- Create a new project in your favourite office application
- Add a VBA reference to the Dynamic RibbonX library (Tools->References)
- The library is now ready to use. In the immediate window enter
Writing some code!
It is recommended that you go through the examples below in the order in which they appear, as each example builds up on previous ones.