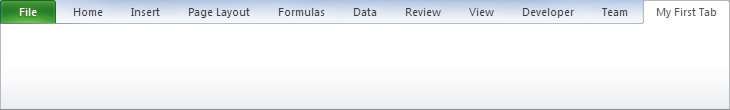
A 'hello world' VBA program
From Ribbon Commander Documentation
Creating a tab
- Enter the code below in a standard VBA module
Public Sub CreateMyUI()
' Get a reference to the default rxCustomUI instanceDim myCustomUI As rxCustomUI
Set myCustomUI = rxCustomUI.defaultInstance' Get a reference to the rxRibbon object of our rxCustomUI instanceDim myRibbon As rxRibbon
Set myRibbon = myCustomUI.ribbon' Create a new tabDim myTab As rxTab
Set myTab = myRibbon.tabs.Add(New rxTab)
' Give the new tab a labelmyTab.Label = "My First Tab"' Render the UImyCustomUI.Refresh
End Sub
Code Analysis
Dim myCustomUI As rxCustomUI Set myCustomUI = rxCustomUI.defaultInstance
rxCustomUI is at the top of the object model hierarchy. Here, we are holding on to the default rxCustomUI instance for the current office application session.
' Get a reference to the rxRibbon object of our rxCustomUI instance Dim myRibbon As rxRibbon Set myRibbon = myCustomUI.ribbon
Each rxCustomUI object owns a unique rxRibbon object. Here, we are holding on to the rxRibbon object of myCustomUI
' Get a reference to the rxRibbon object of our rxCustomUI instance Dim myRibbon As rxRibbon Set myRibbon = myCustomUI.ribbon